Nylon is the first man-made synthetic fiber. Synthetic fibers are called man-made fibers because they do not come directly from nature, they come synthetically. It is a type of polymer compound, which is the sum of many monomers. It is a polyamide fiber. Polyamide is formed by the process of polymerization of a substance. This polyamide is called nylon. This polyamide is a long-chain synthetic polymer with amide linkage connected by two aromatic rings.
Table of Contents
What is nylon fabric?
Nylon is the name of a genus of synthetic polymers that are used to make a variety of clothing and consumer goods.
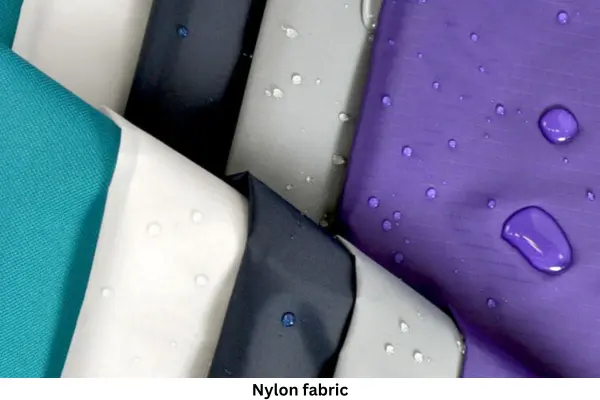

Unlike other organic or semi-synthetic fibers, nylon is a completely synthetic fiber which means that nylon fibers have no resemblance to organic fibers.
History of Nylon Fabric
- 1927 Firstly Research in polymer, and was announced in 1938.
- This polymer was shortly published at the New York World Fair in 1939.
- Charles Stine gave a structure of polymer in 1927.
- Carothers and his team published a new project and this is synthesized two new polymers in the spring of 1930. One is a synthetic rubber that’s called
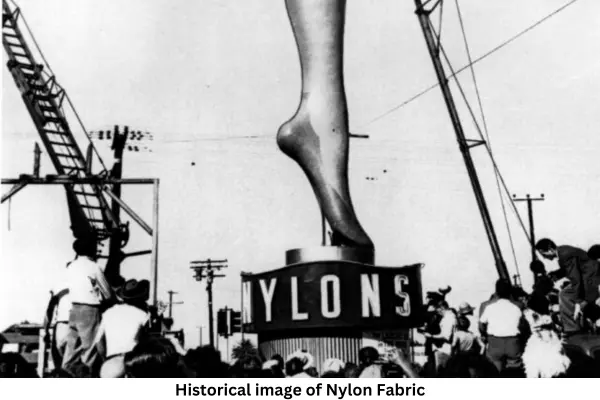

- neoprene and other was a white elastic after form nylon.
- Then polymer 6-6 was produced in 1935 and in this time fully develop nylon.
- The polymer production industrially in September 1938,[22] and quickly achieved a monopoly of the fiber.
- After that commercial production of polymer on December 15, 1939.
Properties of nylon fabric
- Polyamide is the repeating unit of Nylon.
- The functional group ―CONH― in a ring contains the main chain of the polymer.
- Do not soluble in water
- May create static electricity
- It can melt at high temperatures.
- Feel looks like silk fiber.
- It is a stronger fiber than natural fiber.
- It blended with cotton to create resistance in the fabric
- Looking is very attractive to consumers.
- Nylon fiber is less comfortable than natural fiber.
Physical Properties
- Tenacity: For the Nylon fiber the tenacity is,
- Dry Condition = 3.5 to 7.0 (g/d),
- Wet Condition = 2 to 6.2 (g/d),
- Elasticity: Nylon Fibre elasticity is Very Good and Breaking extension is 20-40%.
- Stiffness: The stiffness of the Nylon fibre is = 17 to 20 (g/d).
- Moisture regain: In the case of the Nylon Fibre moisture regain,
- @ 65% RH, 3.5 to 5 %
- @ 100% RH, 3.5 to 8.5 %
- Specific gravity: 1.14.
- Abrasion resistance: Excellent.
- Dimensional stability: Good.
- Resiliency: Excellent.
- Softening point: Nylon 6,6 – 2290C, Nylon 6 – 1490C.
- Melting point: Nylon 6,6 – 2520C, Nylon 6 – 2150C.
- The hand feel: Soft and smooth
Chemical properties of nylon
- Acid: Nylon six,6 is attacked by mineral acids and it is dissolved nearly. but is inert to dilute acetate acid and formic acids even at a boil. Nylon six is attacked by mineral acid and it is always resistant to dilute boiling organic acid.
- Bleaches: Nylon is not attacked by oxidizing and reducing bleaches.
- Alkali: Nylon is significantly inert to alkalis.
- Organic solvent: Most of the solvents have little or no result on nylon.
- Light: No discoloration. Nylon six steps by step loss of strength on the prolonged extension.
- Biological: Neither little organisms nor insect, larvae attack nylon.
- Electrical: It has High insulating properties and finally ends up in static charges on the fiber.
- Flammability: Burns slowly.
Different types of nylon
- 1. Nylon 6: [NH−(CH2)5−CO]n made from ε-Caprolactam.
- 2. Nylon 6 10: [NH−(CH2)6−NH−CO−(CH2)8−CO]n made from hexamethylenediamine and sebacic acid;
- 3. Nylon 510:Made from pentamethylene diamine and sebacic acid
- 4. Nylon 1,6: Synthesized from dinitriles using acid catalysis
- 5. Nylon 6,6: [NH-(CH2)6−NH−CO−(CH2)4−CO]n−[NH−(CH2)5−CO]m made from caprolactam, hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid
Different types of nylon fabric
- Nylon 7.8: Such polymers were initially completely synthetic fibers.
- Ninel 7: This type of polymer is sometimes used to make nylon fabric. But it is used less than nylon 7.6.
- Nylon 4,8: This type of polymer is produced by International Corporation psm and it is marketed under the name Steel. It is commonly used in engine components such as transmission, brakes, and air conditioning systems.
- Nylon 5,10: It is commonly used instead of nylon 7.8. It is primarily used in scientific work in the industry.
- Nylon 1,6: This polymer adiponitrile is made from a mixture of formaldehyde and water but it is not used in fabric and general use.
Made of nylon
Nylon is made using coal, water and air. Some acids and amine compounds are made from these materials, which later take the form of nylon. The main raw material for making nylon is:
- 1. Hexamethylene di amine
- 2. Adipic acid
The polymerization of these compounds is initiated by the condensation process. Thus the acid and alkali ratio in the nylon salt obtained when they are bonded to each other is 1: 1. The salt is then nitrated and dried again. The steps take the form of nylon.
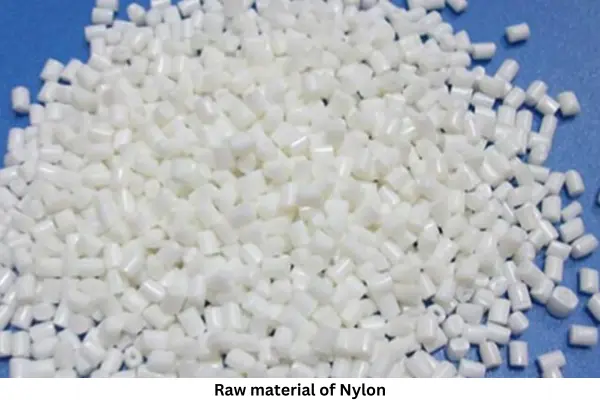

Adipic acid: It is an organic compound with the symbol (CH2) 4 (COOH) 2. From a business point of view, it is the most important dicarboxylic acid. Adipic acid is a bipolar acid because it can supply twice as many protons. Its pKa’s are 4.41 and 5.41. Adipic acid exhibits intermolecular condensation reaction due to the carboxylate group separated by four methylene groups, in reaction with barium hydroxide it provides cyclopentane through ketonization.
Hexamethylene diamine: Organic diamine contains amino radicals on both sides of the carbon molecule.
How is nylon fabric made?
- 1. Extraction of di-amide acid: Monomers called di-amide acid have to be extracted from crude oil.
- 2. Mixture: A polymer called nylon salt is formed by reacting di-amide acid with adipic acid.
- 3. Warm-up: The crystalline object has to be turned into a molten object by successive heat.
- 4. Expulsion: The object is then extruded with a metal weave.
- 5. The burden: The extruded object is loaded with a type of scraper called a bobbin.
- 6. Stretch: That fiber is then stretched to increase strength and elasticity.
- 7. Pulled: Then it is pulled through the reed.
- 8. Rotation: The resulting fiber is then twisted into a garment or other type of fiber.
- 9. Finish: The resulting yarn is dyed and turned into the desired product.
Benefits of using nylon
- i) Nylon yarn is much stiffer and elastic or elastic. So it is used to tie something stiff.
- ii) It is possible to go up and down the hill using nylon rope.
- iii) Nylon is light so its rope can be easily washed.
- iv) Nylon is used as parachute rope.
- v) The color of nylon is very bright. It can be given any color.
- vi) Nylons do not hold too much water but they can hold our body heat.
You may also like to read:
