Man-Made Fiber means the fiber which is made by a human. Actually, fiber basically made in a laboratory from a natural fiber that’s called man-made fiber.
Table of Contents
History of Man-made fiber:
At the beginning of the nineteenth century, just as all scientists were busy discovering one by one, a French scientist named Hillary de Cadonet began researching fiber, and he first created a new type of fiber from wood, the bark of a tree. Named as viscose. Cellulose was dissolved in a “viscose” solution, hence the name “viscose fiber”.
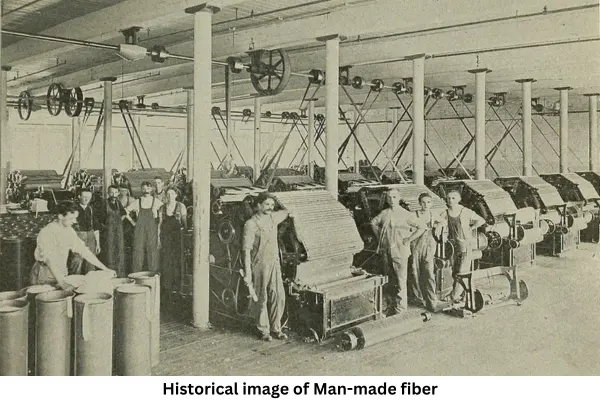

It is also known as “Viscose Rayon”. In 1893, Charles Frederick Cross and Edward John Beven introduced “Viscose Rayon” to the world through extensive research.
What is Viscose Rayon?
A solution of honey-like liquid is obtained by dissolving the cellulose obtained from wood, tree bark, and bash in a solution called viscose.
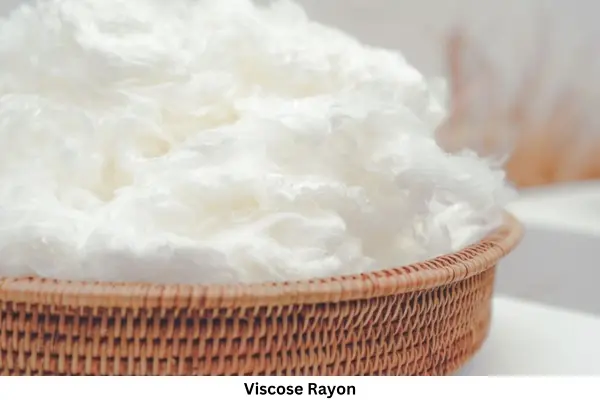

By generating this liquid solution and entering the spin rate, a type of fiber is formed. This fiber is known as viscose. It is also the most popular as “Rayon”.
Different types of viscose rayon depend on the production
Since the creation of viscose, scientists have tried to make it in different ways and they have succeeded. In this series, we have found different types of viscose at different stages. Due to the differences in the production process, Vasco da Gama can be divided into different parts. Man-Made Fiber
1) Nitrocellulose:
The earliest viscose produced from cellulose is nitrocellulose. The most expensive is viscose rayon. It was also developed as “artificial silk” in 1855. Due to the high cost, its use was greatly reduced. The use of nitrocellulose was discontinued in the early 1900s due to the high cost.
2) Acetate Rayon:
Although the chemical composition of acetylene is slightly different from viscosity, it is produced from cellulose-like acid. As it is produced from cellulose, acetate is included in the types of rayon K and viscose. Acetate rayon is usually formed as a result of a mixture of cellulose and acetic anhydride.

3) Caprium Rayon:
Cellulose is dissolved in a solution of premium hydroxide and premium rayon is formed. Production began in the 1900s. It looks a lot like silk fabric.
4) Modern process:
Charles Frederick produced Ray using cross carbon dioxide and gents. The cheapest process ever produced is the modern method of producing Rayon. Viscose produced in this process is therefore the most common.
5) Lyocell:
The viscose that is usually obtained by dissolving cellulose in a solution of “methyl morphine n oxide” is called lyocell ion
The production method of Man-Made Fiber:
These are just some of the goal-setting shareware that you can use:
- 1) Cellulose extraction
- 2) Conversion of cellulose to alkali
- 3) Pressure
- 4) Maturity and Generation
- 5) Turn
- 6) Filtering and extruding
- 7) Combination with acid
The details of each step are given below:
1) Cellulose Extraction:
90 percent cellulose is needed to make the disc. The process of making cellulose from bash, wood, tree bark is started as well as the process of making rayon.
2) Cellulose conversion to alkali:
Cellulose is usually dissolved in caustic soda solution and cellulose is converted to alkaline cellulose by chemical reaction.
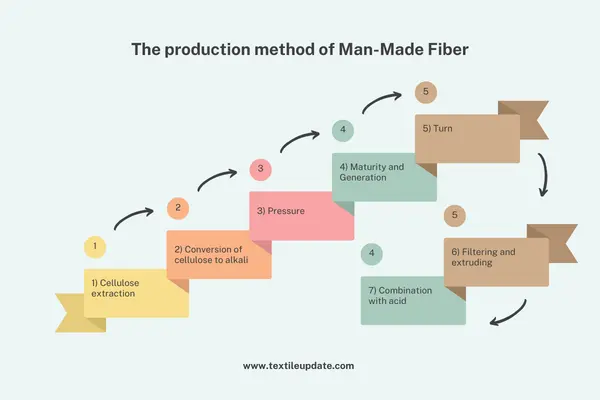
3) Pressure:
Alkaline cellulose is removed by pressing the liquid through a roller. The “white order” substance is added to the amount of alkali that remains in the solid state after it has been removed.
4) Maturity and Jantheshan:
The alkaline “white order” is matured by oxidizing in contact with oxygen. It then reacts with carbon dioxide to form the “yellow order”.
5) Adaptation:
The “yellow chrome” is turned into a solution and within a few hours, the solution becomes suitable for filtering.
6) Filtering and Extruding:
After turning yellow chrome, it is filtered and if any bubbles are created as a result of the filter, those bubbles are removed. When the removal process is complete, the alkali is extracted with the help of spinrate.
6) Acid composition:
Filaments are made by mixing the resulting product with a solution of sulfuric acid. After washing this filament the desired fabric is obtained.
Features of Man-Made Fiber:
Viscose has some features that set it apart from other fabrics. The following features are mentioned-
- 1) Usually the thread count variation of viscose is 300 to 600.
- 2) Viscose fabric breathability is very high quality.
- 3) The moisture ability of this fabric is very good.
- 4) The fabric can hold a lot of heat.
- 5) The expansion capacity of this fabric is of medium quality.
- 6) The chances of peeling or bubbles are moderate.
Uses of Man-Made Fiber
- We can use viscose in a variety of ways, sometimes with cotton, sometimes with silk, and sometimes for industrial purposes.
- Usually, due to the combination of cotton, many people cannot distinguish between this fabric and cotton. With the help of rayon, we can make shirts and pants. It is also very popular for making washcloths and tablecloths.
- A lot of the time in industrial work we use this rayon to make tires. Because it is much cheaper. It is also used to make belts.
- It is usually combined with silk to make smooth garments like scarves, nightgowns, etc.
Benefits of using Rayon
- 1) It is very glamorous to look at.
- 2) Prices are much cheaper.
- 3) It is usually dustproof.
- 4) It is much more durable.
- 5) It does not need to be cleaned as much as other fabrics.
Difficulties
- 1) The use of such clothing can cause breathing problems.
- 2) It folds easily.
- 3) The clothes made in this picture cannot be cleaned together. It has to be cleaned separately. It costs a bit more.
- 4) The level of environmental pollution is much higher during the production of this fabric.
May you also like to read:
Linen Yarn: History, physical and Chemical properties, uses & Characteristics
